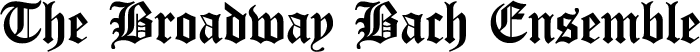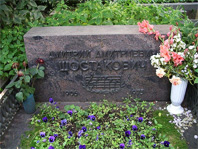20th Century, Overture, Works
Francis Poulenc was part of a prominent group of early 20th-century French composers dubbed “Les Six.” A self-taught composer, his music is unconventional, with understated wit and simplicity. In 1918, while serving in the French army, he wrote a four-hand sonata for piano which was premiered in 1919 and revised in 1939. Darius Milhaud (also a member of “Les Six”) was much taken by Poulenc’s sonata, and orchestrated the last movement for a concert he conducted in 1923 with the Philadelphia Orchestra.
It is a short, playful work. As a contemporary reviewer put, “High spirits, wit and animal grace break out of the merry brass in the ‘Overture.’”

20th Century, Concerto, News Flash, Works
The violin concerto was Barber’s first significant commissioned work. Barber began composing the concerto in 1939 while on a trip to Switzerland. Upon the outbreak of World War II, he returned to the United States and completed the concerto later that year. The concerto was premiered by Albert Spalding with the Philadelphia Orchestra in 1941. Ever since then, it has been a staple of the violin concerto repertoire.
Barber provided these program notes for the premiere performance:
The first movement — allegro molto moderato — begins with a lyrical first subject announced at once by the solo violin, without any orchestral introduction. This movement as a whole has perhaps more the character of a sonata than concerto form. The second movement — andante sostenuto — is introduced by an extended oboe solo. The violin enters with a contrasting and rhapsodic theme, after which it repeats the oboe melody of the beginning. The last movement, a perpetuum mobile, exploits the more brilliant and virtuosic character of the violin.

20th Century, Concerto, News Flash, Works
Béla Bartók (1881-1945) completed the sketches for his viola concerto shortly before his death in New York from leukemia in 1945. He had been commissioned to write the concerto by William Primrose, the great Scottish violist. Bartók wrote to Primrose shortly before his death that the concerto had been fully sketched out and only required a few weeks to be orchestrated, but he died before this work could be completed. At the request of the Bartók family, it fell to Tibor Serly, Bartók’s close friend and colleague, to write the orchestrations and finalize the concerto for publication. It took four years for Serly to finish this task, owing largely to the fragmentary nature of Bartók’s sketches, which were written on 13 unordered pieces of paper. The concerto was premiered by Primrose in 1949. While a number of subsequent revisions have been done (including one by Peter Bartók, the composer’s son), the original Serly version has remained a beloved staple of the viola literature ever since.
The concerto has three movements, played without a break. The opening Moderato begins with a lyrical four-bar theme in the solo viola, accompanied by ‘cello and bass. The theme is taken up by the winds in turn, and appears several times in the course of the movement. A contrasting triplet-based theme appears twice, accompanied by syncopations in the orchestra.
A short declamatory section (lento parlando) and a bassoon solo serve as a bridge to the short second movement. Titled adagio religioso, it is a quiet sustained slow movement, with a short agitated middle section featuring woodwind trills. A sudden solo viola accelerando brings us to a lively allegretto, punctuated by horns and timpani.
The rollicking last movement is based on a Rumanian Scottish-influenced melody appearing in contrast. Brilliant viola bring this work to a satisfying conclusion.

20th Century, Symphony, Works
In 1936, after a performance of “Lady MacBeth of the Mtsensk District,” an article in “Pravda,” the Russian newspaper of the time, publically denounced Shostakovich. The article, often attributed to Joseph Stalin, entitled “Muddle or Music,” claimed that Shostakovich had “missed the demands of Soviet Culture to banish crudity and wildness from every corner of Soviet life.” It went on to say, “The danger of this tendency in Soviet music is clear. Leftist ugliness in opera is growing from the same source as leftist ugliness in painting, poetry, pedagogy, and science. Petit bourgeois ‘innovation’ is leading to a gap away from true art, science … literature.”
During this time period in Soviet history, all art was expected to fit within the confines of Socialist Realism. Socialist Realism dictated that everything be in support of Communism. Music and art were to enhance and support the government, not cause tension or spur acts of rebellion.
Shostakovich feared for his life, as artists who flew in the face of social norms often found themselves executed or banished. Perhaps the only thing that saved him was the fact that in the early 1930’s Shostakovich had written a score to a movie entitled “Counter Plan,” which was released for the 15th anniversary of the October Revolution. One song from that score, “The Morning Greets Us,” gained international acclaim and became the first Soviet song to be considered a hit. This is perhaps the only thing that saved Shostakovich from a gruesome fate.
Composed between April and July of 1937, the 5th Symphony was Shostakovich’s response to the events of the year before. Premiered on November 21, 1937, it was received with thunderous applause that lasted more than half an hour.
Shostakovich had no choice but to claim that the piece was nationalistic in nature. In fact, Shostakovich likely viewed the piece as his chance to regain favor with the Communist party. The last movement quotes a song Shostakovich wrote earlier in the 1930’s, based on a poem by Pushkin, which deals with rebirth. Later on in his memoirs, however, he explained that he wrote the piece in direct response to the persecution and oppression that existed under Stalin’s rule. Since the time of its premiere this symphony has become one of the staples of the classical repertoire and is considered one of the greatest works of the 20th century.
As you listen, you will hear moments of terror, pain, pleading, and downright despair; but out of these moments, Shostakovich gives us wonderful glimpses of hope and in the last movement a feel of redemption and even victory.
(Christopher Hisey)
20th Century, Songs, Works
The Four Last Songs were among Richard Strauss’ last works. He composed them in 1948, shortly before his death. They are all set to poems, three of them by Hermann Hesse — Frühling (Spring), September, and Beim Schlafengehen (While Falling Asleep) — and one of them by Joseph von Eichendorff — Im Abendrot (At Twilight). These were not initially conceived of as a set of songs, but published in that form after his death and premiered in 1950.
The words and music are calm and contemplative; the last three songs evoke an acceptance of death. The music features melodic interplays between the soprano and the orchestra, subtle chromatic shifts, and lyrical horn passages.
(M. F. Tietz)

20th Century, Concerto, Works
This concerto was dedicated to Marcel Moyse.

20th Century, Concerto, Works
Astor Piazzolla (1921-1992) was one of Argentina’s most gifted and prolific composers. He started out as a self-taught composer and accomplished player on the bandoneon, an Argentine variant of the concertina/accordion. After formal composition study in Paris he returned to Argentina and revived tango in a modern “nuevo tango” form.
He wrote the four movements of the Cuatro Estaciones Porteñas (Four Seasons of Buenos Aires) between 1965 and 1970 for his tango instrumental quintet (violin, piano, electric guitar, bass and bandoneon). They were conceived as separate pieces, although Piazzolla occasionally performed them together.
In the 1990s, violinist Gidon Kremer commissioned the Russian composer Leonid Desyatnikov to arrange these four compositions for solo violin and string orchestra. Otoño Porteño is the third of these. It is characterized by brilliant passages for the solo violin, strong pulsing rhythms/syncopation, and wistful slow interludes for solo ‘cello and solo violin.
20th Century, Suite, Works
This work began as a film score. In 1934 Prokofiev was commissioned to compose a score for Lieutenant Kijé (in Russian, Parootchik Kizhe), a movie satirizing the military and bureaucracy in Czarist Russia.
The plot is based on a mythical tale that hinges on a spelling error. In the film, a clerk misspells a phrase while copying out military orders: the Russian phrase “parootchiki, zheh” (“the lieutenants, however…”) becomes “Parootchik Kizheh (“Lieutenant Kizheh”). The Czar reads the orders and thinks there is a “Lieutenant Kijé” in his guard company!
Not daring to tell the Czar about the copying mistake, the Czar’s aides, courtiers and military officers instead fabricate an entire life for the “Lieutenant.” Besides a military career, they concoct a romance and even a marriage for him.
The fictional lieutenant rises high in the Czar’s esteem and is rewarded with promotions and riches. Finally, the Czar’s aides devise a way to “kill off” the non-existent lieutenant, and he is buried with military honors.
By 1937 Prokofiev reworked the movie score into a substantial five-movement suite, each depicting a scene from the fictional lieutenant’s life. It begins with the “Birth” of Kijé, featuring a far-off trumpet solo and martial music.
This is followed in succession by a Romance based on a love song (featuring a double bass solo); Kijé ‘s marriage, with a flourish of brass, pomp and ceremony, followed by a lively trumpet tune; the famous Troika, evoking a winter sleigh ride in the snow; and, finally, Kijé ‘s death and burial, in which brief passages from the other movements serve as reminiscences of his fictional “life.”
The suite ends as it began, with a trumpet solo in the distance.
20th Century, Suite, Works
Stravinsky orchestrated this suite for small orchestra based on simple tunes he initially composed for the piano between 1914 and 1917. It is one of many “miniature” works that Stravinsky composed during his life, experimenting with various combinations of instruments, styles and textures.
This short work is in four movements — an opening calm Andante; the rollicking “Napolitana,” evoking an Italian street song and featuring woodwinds; an intense Española, with jagged rhythms, offbeats and contrasts; and the final Balalaȉka, tuneful throughout, with an abrupt ending.
20th Century, Concerto, Works
This happy, exuberant piece was composed by Shostakovich in 1957 for his son Maxim’s 19th birthday. It was premiered that year by the Moscow State Philharmonic, with Maxim as the piano soloist after his graduation from the Moscow Conservatory.
The work is in three movements. The woodwinds start the sprightly allegro, quickly joined by the piano in the opening four-note theme, with bursts of hammering percussive passages.An introspective lyrical second theme follows, with the piano accompanied by soft strings. A development section and return to the initial theme bring the movement to a close.
The middle movement is by turns wistful, poignant and lyrical, with singing piano themes that evoke late 19th-century romanticism. The piano opens the final sparkling allegro with octave-based flourishes and scales. Following that, a rollicking second theme (in 7/8 time) is heralded by the winds, in turn picked up by the piano and the strings.
On a pedagogical note, Shostakovich included many scale and arpeggio passages ‑ based on piano exercises by Louis Hanon ‑ to make sure that Maxim would learn them! Those passages are in turn echoed by the strings. A recap of the main theme, strong brass-led chords, and a timpani flourish bring this sparkling concerto to its close.